
Second aspect : Muscle strength is affected from mild to severe, graded from 5 to 0 as follows:ĥ: Can resist gravity, complete all joint activities, and resist the greatest resistance.Ĥ: Can resist gravity, complete all joint activities, and resist some resistance.ģ: Can resist gravity and complete all joint activities.Ģ: Can complete all joint activities on a flat surface without gravity.ġ: No activity, but muscle contraction can be palpated.Ġ: No activity and no muscle contraction. The symptoms and progression of the disease usually include the following three aspects: sensation changes, muscle strength changes, and characteristics of the compression source.Âįirst aspect: refers to the sensation changes, which progress from tightness to soreness, aching, dull pain, stabbing pain, tearing pain, and eventually numbness. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is divided into two types Pain and limited range of motion may occur with certain movements or angles, while other movements may not cause discomfort.Increased activity may lead to increased discomfort.Prolonged fixed positions can cause discomfort, but moving the body can provide relief.Common Situations with Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Please click here to schedule an appointment.

It is recommended to schedule a physical therapy evaluation to assess the underlying causes and provide appropriate treatment. These factors can all lead to muscle tightness, inflammation, weakness, or other symptoms in the thoracic outlet region.
#Thoracic outlet syndrome sleeping position series
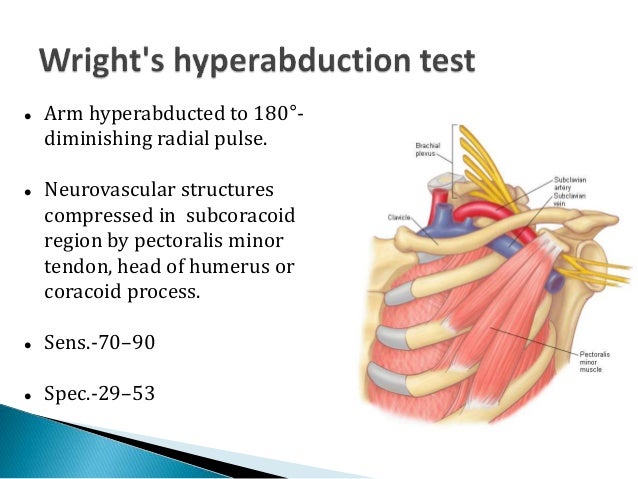
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) refers to a series of symptoms that occur due to compression of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or vein within the narrow space of the thoracic outlet.Â


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
